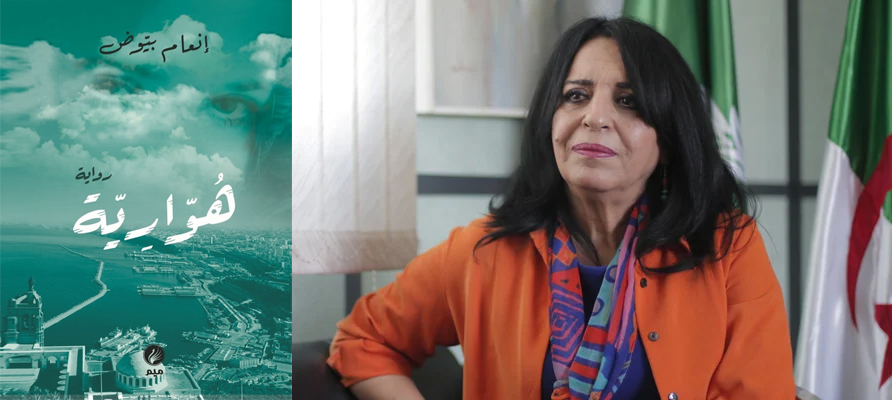Kamel Daoud’s Goncourt-Winning ‘Houris’ Breaks the Silence on Algeria’s Black Decade
For countries sharing as complicated a relationship as France and Algeria, some might expect the recent awarding of France’s most prestigious literary prize, the Prix Goncourt, to an Algerian writer to be cause for celebration. Algerian-born writer Kamel Daoud emerged the winner of this year’s Goncourt with his third novel “Houris” (“Virgin” in English), securing six out of 10 votes from Académie members during the deliberation process.
Decline, Displacement, and Despair Have Stifled the Mesmerizing Glow of Al Hamra Street
Ongoing talks of the nostalgic past and less depressing times bring to mind Beirut’s own miniature ‘Andalusia,’ its famous Al Hamra Street, which — like the majestic Andalusia of eld — has become an unachievable, distant relic of a flourishing time.
‘Is There an Arab Culture?’
Long History of Pluralism, Decentralization, Pragmatism Underpins ‘Arab Culture’ Debate
Rarely do we read a cultural or even general-interest publication without encountering discussions questioning whether an Arab culture exists, and if it exists, whether it is in decline. I found no exception when recently perusing Al Jazeera’s online cultural section. We do not need to look far into the article, as its title speaks for itself: “Is There an Arab Culture?” The article is by Dr.
Dreadful Days in Lebanon: The Invisible and Visible Scars of War
Discussing and analyzing the catastrophic disaster that hit Lebanon is difficult. I am connected to the subject on two levels: intellectually and emotionally. Hamas' "Operation Al-Aqsa Flood" and Hezbollah's "Operation of Solidarity" have been viewed as irresponsible, and their military consequences questionable, with the conflict leaving unprecedented emotional scars on many Lebanese.
Literary Awards Determined by Craftsmanship or Politics?
Imprisoned Palestinian Author Basim Khandaqji’s Win Reignites Old Questions About Booker Prize Standards
It would be remiss to overlook the significance that this year’s chosen winner for the International Prize for Arabic Fiction (Booker), one of the Arab world’s most prestigious literary awards, was written by an imprisoned Palestinian writer. When the prize committee announced the victory of Basim Khandaqji’s “A Mask, the Color of the Sky” (Dar al-Adab, 2023) in April, six months after Israel’s attacks on Gaza began, media outlets were quick to recognize Khandaqji’s daunting feat of publishing from jail.
Trapped in the Cage of the Past, Algeria Must Navigate the Line Between Memory and Moving Forward as Paris Olympics Stirs French-Algerian Wounds
Algeria has much to celebrate with the end of the 2024 Olympic Games in Paris, taking the podium in gymnastics, boxing, and athletics. Yet while the country celebrates the victories, its athletes share the spotlight with headlines focusing on the country’s history with France.
Novel 'Houaria' Forces Algerian Critics into a Literary-Ideological Battle Armed with Morality and Ethics
A familiar debate has critics and writers up in arms in the Arab world once again: What place does ‘taboo’ have in art? Ethics, morality, and the sensibilities of the contemporary age are yet more factors that play into creative production these days.